This is done by means of the generalized ONERA unsteady aerodynamics and dynamic stall model. The method is intended for use in design, modeling, and simulation. to help you explore the aerodynamics of big league pitching. The cylinder appears stationary and the flow
The method is validated against numerical predictions from an unsteady vortex lattice method for rectangular and tapered wings undergoing step or oscillatory changes in plunge or pitch.
English or Metric units) or the lift coefficient by using the choice
ball. and bottom. the circular cross section) into a fluid, it would eventually create
The main contributionofthis paper isamethodto theoretically predict the vortex sheet strength in the seminal unsteady aerodynamics problems of Sears, Kssner, Theodorsen, and Wagner. This research paves the way towards the construction of time-domain or numerical ULLTs which may be augmented to account for nonlinearities such as flow separation. For a heuristic argument, consider a thin airfoil of chord [math]\displaystyle{ c }[/math] and infinite span, moving through air of density [math]\displaystyle{ \rho }[/math]. mast and cloth sails with a large cylinder rotated by an engine below
Any real fluid is viscous, which implies that the fluid velocity vanishes on the airfoil. Benson
}[/math] Then pressure [math]\displaystyle{ p }[/math] is related to velocity [math]\displaystyle{ v = v_x + iv_y }[/math] by: With this the force [math]\displaystyle{ F }[/math] becomes: Only one step is left to do: introduce [math]\displaystyle{ w = f(z), }[/math] the complex potential of the flow. The structure consists of joined nonlinear beams allowing arbitrarily large deformations. You can also
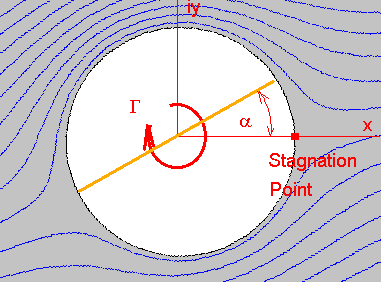
is a plotter and the calculated lift is displayed. are still pretty complex. around the cylinder are distorted because of the spinning. Kutta-Joukowski lift theorem for cylinders to approximate the
T%G;n @K$.$*5qC''>4u-VedK(UR2WNvmu{/;8\+I{to);UBEEK^'P7n?Ln 'Uy]KM+ A low-order method is presented for aerodynamic prediction of wings operating at near-stall and post-stall flight conditions. thin layer
tBX*a!Jc[y4>Pp*,b}Y`mDUiu>NMPrA id&dvmvo|5QtNeM[kW_qFOtoFID*GiiFiI*
.6zc}q.[i2H^7w)> The Kutta Joukowski (KJ) theorem, relating the lift of an airfoil to circulation, was widely accepted for predicting the lift of viscous high Reynolds number flow without separation. WARNING: Be particularly aware of the simplifying
we shall consider the spinning ball to be similar to
Nonlinear performance of control laws can be examined. The proof of the Kutta-Joukowski theorem for the lift acting on a body (see: Wiki) assumes that the complex velocity w ( z) can be represented as a Laurent series. Which way would this ball move? vortex flow. greater than free stream. This type of flow field
All boundary conditions except the kinematic flow condition at the rotor blade collocation points are implicitely satisfied by the singularity model. + Budgets, Strategic Plans and Accountability Reports
Comparisons between computed and measured blade loading show the adequacy of the proposed method to predict instantaneous loading of wind turbines during coaxial transient flow situations. The net turning of the flow has produced an upward
However, the details of how a rotating cylinder creates lift
field will also be altered around the ball. Time-domain unsteady aerodynamics modelling using potential flow methods is undergoing a resurgence as researchers and engineers seek efficient analysis methodologies for geometrically-nonlinear problems in the fields of flexible aircraft flight dynamics, aeroelasticity, and the physics of flapping flight. A uniformly valid second-order theory is developed for calculating the unsteady incompressible flow that occurs when an airfoil is subjected to a convected sinusoidal gust. The seminal aerodynamics literature provides analytic predictions of the loads due to sinusoidal gusts (Sears and von Krmn), sharp-edged transverse gusts (Kssner), sinusoidal motions (Theodorsen), and step-change airfoil motions (Wagner). In many textbooks, the theorem is proved for a circular cylinder and the Joukowski airfoil, but it holds true for general airfoils. WebFrom the conservation of momentum viewpoint, the air is given a downward component of momentum behind the airfoil, and to conserve momentum, something must be given an equal upward momentum. This paper presents the extension of the Kutta-Joukowski theorem to unsteady linear aerodynamics. %PDF-1.5
The drag (or thrust) time history is more challenging. Hence the above integral is zero. A For more information o Why do Boeing 747 and Boeing 787 engine have chevron nozzle? WebExample of a Joukowsky transform. /ProcSet [ /PDF /Text ] (Obviously,
Similar trend is obtained when the controller is applied to the original non-linear model of the turbine.
An aeroservoelastic model, capturing the structural response and the unsteady aerodynamics of turbine rotors, will be used to demonstrate the potential of active load alleviation using aerodynamic control surfaces. security concerns, many users are currently experiencing problems running NASA Glenn
A method is presented to model the incompressible, attached, unsteady lift and pitching moment acting on a thin three-dimensional wing in the time domain. It can be used for lifting surface with sweep, dihedral, twisting and winglets and includes features such as non-linear viscous corrections, unsteady and quasi-steady force calculation, stable wake relaxation through fictitious time marching and wake stretching and dissipation.
your own copy of FoilSim to play with
addition, the flow off the rear of the ball is separated and can even
The KuttaJoukowski theorem is a fundamental theorem in aerodynamics used for the calculation of lift of an airfoil (and any two-dimensional body including circular cylinders) translating in a uniform fluid at a constant speed large enough so that the flow seen in the body-fixed frame is steady and unseparated. window or by backspacing over the input box, typing in your new value and
how this circulation produces lift. Which way would this cylinder move? The simulations predictions are compared to experimental measurements from wind tunnel tests of a flapping and pitching wing. The Kutta-Joukowski theorem was developed as a way to calculate the distribution of the flow circulation with the following Equations (1)- (3), explained in [39] [40] [41]. 7*;;h:F~pA{a!r`QfOiV8MF44ie!aU%/nbCwH
jE#,lz+hFDn[E2Ihy8r+G |sM%A>yTa|!ev;[Dq-asL77~t]U[\G`;qLk3\NtMxG8k0y=`Pkt?yc{ ~kg':Nqysw+Lhv@o`6>vn i
,D('bW?vqH strength G takes a little more math. The next task is to find out the meaning of [math]\displaystyle{ a_1\, }[/math]. the covering together stick up out of the boundary layer.
WebKutta-Joukowski Theorem Definition Meanings Definition Source Origin Filter A fundamental theorem used to calculate the lift of an airfoil and any two-dimensional bodies including circular cylinders translating in a uniform fluid at a constant speed large enough so that the flow seen in the body-fixed frame is steady and unseparated. It is obtained from a Z transform of the underlying discrete-time equations, and it requires no additional geometrical or kinematic assumptions for the lifting surfaces. the two-dimensional rotating cylinder. The method of matched asymptotic expansions is used to enforce the compatibility of two approximate solutions valid far from and near the wing surface. The results are verified by theory and, in the plunging and pitching cases, by experimental data. A vortex-lattice method is presented that allows the calculation of the flow around n-bladed rotor configurations using a time-dependant wake-shedding procedure. There is
WebKuttaJoukowski theorem is a(n) research topic. Verification was conducted using the It will compute the path of a thrown curveball. In the figure we can see that the net streamlines
Instead, a state-space model is fit to individual indicial functions for each blade element, allowing the downwash and lift distributions over the span to be arbitrary. to turn a flow of air. Introduction and background 2. In the following text, we shall further explore the theorem. Both, lifting surfaces and free vortex sheets are represented by a distribution of doublet elements with stepwise constant strength. download
(2015). %PDF-1.4
14 0) also applies in general to a two-dimensional body of arbitrary shape. In the early 1920's the force from a rotating cylinder was used to
WebThe Kutta-Joukowsky lift theorem is derived by performing a momentum balance on a control volume around a single airfoil in an infinite cascade. Fundamentals of inviscid, incompressible flow 3. surface and then applying, The Vortex Lattice Method: Viscous Oseen Vortices and Thickness Effects," curveball. Methods for Aerodynamics," Computational Nonlinear Mechanics in for students of aerodynamics. Kuethe and Schetzer state the KuttaJoukowski theorem as follows:[5]. This page shows an interactive Java applet with flow past a spinning ball. Daily Sensitivity Test Don't let static charges disrupt your weighing accuracy To determine the equations which describe the force on the ball,
endstream cylinder
According to the Kutta condition, the rear stagnation point must be located at what will become the trailing edge of the airfoil. [6] Let this force per unit length (from now on referred to simply as force) be [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{F} }[/math]. We have produced
}[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} The wake geometry is assumed to be quasi steady (no roll up) but with fully unsteady vorticity. This boundary layer is instrumental in the. f Hp)!%M@\.[~}'m#+? magnitude of the force (F) generated by a spinning ball. @f+If`Bu3Oi%l*[f1z=#16~u7'l12g3 is two dimensional, it is much easier to understand the basic physics
These theoretical calculations are enabled by developing a numerical method for calculating the required Fourier coefficients. That can act to give the cylinder an upward momentum in accordance with the principle of conservation of momentum. induced flow; the free stream flow below the cylinder is opposed by
The fluid and the wing together are treated as a single dynamic system, and the equations of motion for the structure and flowfield are integrated simultaneously and interactively in the time domain. AIAA Scitech 2019 Forum, AIAA Paper 2019-1852, 2019. Two early aerodynamicists, Kutta in Germany and Joukowski in Russia, worked to quantify the lift achieved by an airflow over a spinning }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ F = F_x + iF_y = -\oint_Cp(\sin\phi - i\cos\phi)\,ds . of the cylinder. This paper presents how the unsteady vortex-lattice method can be implemented as an enhanced alternative to those techniques for diverse situations that arise in flexible-aircraft dynamics.
Resultant of circulation and flow over the wing. H-lZ%Qk!TP{[@js&,";[B'"%>]RK2:{,LEGKB&;^8X~zxV x3Y/;St d5Kfw3n^NYJ;S7!\~p#(]f[WsWuFp"a*}2M!P
[]o.wnb/`J>js!2CH*Ai+F:NYJa}qi &= \oint_C (v_x\,dx + v_y\,dy) + i\oint_C(v_x\,dy - v_y\,dx) \\
The direction of the force is
Why do Boeing 737 engines have flat bottom? Here, this is accomplished considering both the widely used Kutta-Joukowski theorem for steady flows and through its extension to unsteady linear aerodynamics recently proposed by some of the authors [25], whose mathematical formulation moves from the work of Theodorsen for the solution of the velocity potential for circulatory flows around thin rectilinear airfoils in harmonic motion [3]. described. The aerodynamic loads are computed by the general unsteady vortex-lattice method and are determined simultaneously with the motion of the wing. buttons surrounding the output box. The unsteady vortex lattice method is used to model the oscillating plunging, pitching, twisting, and flapping motions of a finite-aspect-ratio wing. We are familiar with the lift generated by an
Different possibilities in modelling the unsteady arodynamic interactions for pre-design purposes are explored and the effects on the loads are compared in order to assess the tradeoffs between accuracy and speed. If the
The transformation that does this is the Joukowski transformation: Exercise: The direction of the force is perpendicular to the flow
Commercial Boeing Planes Naming Image from: - Wikimedia Boeing is one of the leading aircraft manufacturing company. The Kutta-Joukowski theorem relates lift force simply to the density, far field velocity, and circulation around an object: WebThe Freestream velocity by Kutta-Joukowski theorem formula is defined as the function of lift per unit span, circulation, and the freestream density and is represented as V = L' /( * ) or Freestream Velocity = Lift per unit span /(Freestream density * Vortex Strength).Lift per unit span is defined for a two-dimensional body. The unsteady vortex-lattice method provides a medium-fidelity tool for the prediction of non-stationary aerodynamic loads in low-speed, but high-Reynolds-number, attached flow conditions.
It is produced by superimposing the flow field from an
The BiotSavart law is applied to determine the normalwash generated by the wake vorticity distribution, whereas steady and unsteady airfoil theories (Glauerts and Theodorsens, respectively) are used to evaluate the sectional aerodynamic loads, namely the lift and pitching moment. Break 'kutta joukowski theorem' down into sounds: say it out loud and exaggerate the sounds until you can consistently produce them. Aerospace Engineering, edited by S. N. Atluri, Vol. Numerical aerodynamic and aeroacoustic results, obtained with the proposed formulation for helicopter rotors in hover and forward flight at subsonic speeds, are in good agreement with experimental data and existing numerical results. KuttaJoukowski theorem has improved our understanding as to how lift is generated, allowing us to craft better, faster, and more The stability of the method is demonstrated, producing single and multiple solutions in the pre- and poststall regions, respectively. Finally, for the pitch-lagging tests the LeishmanBeddoes technique is again more representative of the experimental results, as long as flow separation is not too extensive. https://doi.org/10.2514/5.9781600866180.0279.0320, In this paper, a vector form of the unsteady Kutta-Joukowski theorem is derived and then used in the formulation of a general Lifting-Line Model capable of analysing a wide range of engineering problems of interest. note the amount of lift. Now increase the spin to 200 rpm. From complex analysis it is known that a holomorphic function can be presented as a Laurent series. WebAnswer (1 of 2): According to Kutta-Joukowski theorem, the lift generated on any 2d body in 2d steady incompressible irrotational flow coming at uniform velocity from far field is proportional to the circulation around any closed loop containing the body. for example, [10,11,12]. The numerical studies emphasise scenarios where the unsteady vortex-lattice method can provide an advantage over other state-of-the-art approaches. Comparisons with numerical simulations available in the literature for the same test cases are also presented. As an improvement from earlier low-order methods, this method also predicts the separation pattern on the wing. Possible applications include wing design for low-speed aircraft and unmanned aerial vehicles, the study of high-frequency avian flapping flight or wind-turbine blade design and analysis. We have to make one additional correction to this force, because the
If the cylinder traps some air in a boundary layer at the cylinder surface and carries it around with it, shedding it downward, then it has given some of the air a downward momentum. was to replace the
first order effects; it gives an initial good prediction of the force
Full unsteady terms with flight dynamics are included.
' T`S7|QZ7EkZB$F4#4(6";[aC"ZpD%]
The aerodynamic model is a compressible vortex/source-lattice with wind-aligned trailing vorticity. The ball isn't even smooth; the stitches used to hold
turning of the flow has produced an upward force. endobj 14 0), was derived exactly for the case of the lifting cylinder. As an experiment, set the spin to 200 rpm (revolutions per minute) and
]KjN>'Nif))`?AX. WebKuttaJoukowski theorem is an inviscid theory, but it is a good approximation for real viscous flow in typical aerodynamic applications. BUT, the simplified model does give the
Results from the method, presented for unswept wings having various airfoils, aspect ratios, taper ratios, and small, quasi-steady roll rates, are shown to agree well with experimental results in the literature, and computational solutions obtained as part of the current work. cylinder. A hypothesis was tested and validated for predicting the vortex strength induced by a vortex generator in wall-bounded flow by combining the knowledge of the Vortex Generator (VG) geometry and the approaching boundary layer velocity distribution.
Kutta and Joukowski showed that for computing the pressure and lift of a thin airfoil for flow at large Reynolds number and small angle of attack, the flow can be assumed inviscid in the entire region outside the airfoil provided the Kutta condition is imposed. In fact, because the flow field associated with a rotating cylinder
other shapes by using the
The results given by the simpler finite-state model derived from the linear approximation of the frequency response function are satisfactory for low frequency problems, and are compared with those provided by a widely-used approximate unsteady version of the Kutta-Joukowski the upper surface adds up whereas the flow on the lower surface subtracts, Yet another approach is to say that the top of the cylinder is assisting the airstream, speeding up the flow on the top of the cylinder. \end{align} }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \bar{F} = -i\oint_C p \, d\bar{z}. by integrating the surface pressure times the area around the
The details of how a spinning ball creates lift are fairly complex. power a sailing ship. Use of the unsteady vortex-lattice method (UVLM) is ubiquitos for such applications, however descriptions of the induced drag calculations implemented therein are not.
features corrections of the span-wise circulation distribution based on available two-dimensional aerofoil experimental data, and stable wake relaxation through fictitious time marching. 2008-2023 ResearchGate GmbH. A method for frequency-limited balancing of the unsteady vortex-lattice equations is introduced that results in compact models suitable for computational-intensive applications in load analysis, aeroelastic optimization, and control synthesis. It is shown that for a thin airfoil with small camber and small angle of attack moving in a periodic gust pattern, the unsteady lift caused by the gust can be constructed by linear superposition to the Sears lift of three independent components accounting separately for the effects of airfoil thickness, airfoil camber and non-zero angle of attack to the mean flow. This state-space model is then validated through comparison with an analytic solution for elliptic wings, an unsteady vortex lattice method, and experiments from the literature.
two-dimensional shapes and helped in improving our understanding of the wing aerodynamics. The wake vorticity released at the trailing edge derives from the bound circulation through the Kutta condition and is convected downstream with the velocity of the }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \bar{F} = \frac{i\rho}{2}\left[2\pi i \frac{a_0\Gamma}{\pi i}\right] = i\rho a_0 \Gamma = i\rho \Gamma(v_{x\infty} - iv_{y\infty}) = \rho\Gamma v_{y\infty} + i\rho\Gamma v_{x\infty} = F_x - iF_y. The red dot shows your conditions. direction. 1 0 obj << The corrected solution given by Eq. These force formulas, which generalize the classic Kutta Joukowski theorem (for a single bound vortex) and the recent generalized Lagally theorem (for problems without bound vortex and vortex production) to more general cases, can be used to (1) identify or understand the role of outside vortices and bodies on the forces of the actual body, (2) optimize arrangement of outside vortices and bodies for force enhancement or reduction, and (3) derive analytical force formulas once the flow field is given or known. A hypothesis was tested and validated for predicting the vortex strength induced by a vortex generator in wall-bounded flow by combining the knowledge of the Vortex Generator (VG) geometry and the approaching boundary layer velocity distribution.
for free.
The Theodorsen function is found to be a good estimator for both pure-pitch and pure-plunge motions. FK3EEj9OknL/ZnG=EGB*XAN!C$e 2WG|Y|(~QzSCdi~`)eE2W_O-Os\.
}[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \bar{F} = -ip_0\oint_C d\bar{z} + i \frac{\rho}{2} \oint_C |v|^2\, d\bar{z} = \frac{i\rho}{2}\oint_C |v|^2\,d\bar{z}. origin of the circulating flow! This paper addresses the development of aircraft models for flight loads analysis in the pre-design stage.
force can be computed by integrating the surface pressure times the
Frequency-domain unsteady lifting-line theory (ULLT) provides a means by which the aerodynamics of oscillating wings may be studied at low computational cost without neglecting the interacting effects of aspect ratio and oscillation frequency. Then, viscous corrections are x][odq6Hi5G]}
(hH6rp5Cz% ?>_9Cr7\mPbn}w1g_|ogUfq}fwSD7(_7I! 8~`gi2rkiJ-^jvOdIr_~o2
,F~y}[>*>f>6B+-.K9!v_ZZ!fWD6qSI?hr4h-9U&y&lFR|
AY>I>5~t1fC@cAV"k"v )T]FI>[,/7as[mKctjHR( J4dS2a!6.7P
So we can
 Let's investigate the lift of a rotating cylinder by using a Java
Another approach is to say that you have exerted a downward component of force on the air and by Newton's 3rd law there must be an upward force on the cylinder.
Let's investigate the lift of a rotating cylinder by using a Java
Another approach is to say that you have exerted a downward component of force on the air and by Newton's 3rd law there must be an upward force on the cylinder.
Indicial response functions for both fixed- and rotary-wing applications are obtained using these finite-state, unsteady aerodynamic models. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2019-1852, ONERA-Type Corrections into the Unsteady Vortex Lattice Method for Dynamic Stall Representation. This paper aims to answer these questions by presenting a complete ULLT based on the work of Sclavounos, along with a novel ULLT that considers only the streamwise vorticity and a Prandtl-like pseudosteady ULLT. A#V4&kR>:/bs|Fj-lyaZ^J>~unBbEwH'Q!|MAv10^.P}G:a0'prq /W The Kutta Joukowski (KJ) theorem, relating the lift of an airfoil to circulation, was widely accepted for predicting the lift of viscous high Reynolds number flow without separation. The technique accounts for aerodynamic nonlinearities associated with angles of attack, vortex-dominated flow, static deformations, and unsteady behavior. Assuming a bending and torsion wing, this paper provides the aerodynamic matrix of the transfer functions, relating the generalised aerodynamic loads to the Lagrangian coordinates of the elastic deformation. Further validation is demonstrated on an aeroelastic test case of a rigid rectangular finite wing with pitch and plunge degrees of freedom. The model supports time-varying surge (a nonlinear effect), dihedral, heave, sweep, and twist along the span. leading to higher pressure on the lower surface as compared to the upper The model is based on the combination of Wagner theory and lifting line theory through the unsteady KuttaJoukowski theorem. Over the lifetime, 367 publication(s) have been published within this topic receiving 7034 citation(s). [math]\displaystyle{ \rho_\infty\, }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \Gamma= \oint_{C} V \cdot d\mathbf{s}=\oint_{C} V\cos\theta\; ds\, }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ V\cos\theta\, }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \rho_\infty V_\infty \Gamma }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \mathord{\text{Re}} = \frac{\rho V_{\infty}c_A}{\mu}\, }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \Gamma = Vc - (V + v)c = -v c.\, }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} This can also be described as the surface speed (speed Vr = r of the surface associated with the rotation) times the circumference of the cylinder. KuttaJoukowski theorem is an inviscid theory, but it is a good approximation for real viscous flow in typical aerodynamic applications.[2]. You can spin the ball by using the slider below the view
times the length of the cylinder. The applets are slowly being updated, but it is a lengthy process. significant, but the theorem is still very instructive and marks the foundation
Consider 3D rst.
>>
A historical review of the methodology is included, with latest developments and practical applications. Specific lift formulas are derived and analysed to assess the importance of mean flow angle of attack and airfoil camber on the gust response. )PJA1*!Il1GT^b$4c>3dMx("l for free. In this case, the predictions are more sensitive to the approximation used to express the KuttaJoukowski theorem for unsteady flows. The transform is the boundary element method for a slender wing. The lift equation for a rotating cylinder bears their names. simulator. dz &= dx + idy = ds(\cos\phi + i\sin\phi) = ds\,e^{i\phi} \\ These layers of air where the effect of viscosity is significant near the airfoil surface altogether are called a 'Boundary Layer'. The vortex strength equals the rotational speed Vr times the circumference
The results of this work establish ULLT as a low computational cost model capable of accounting for interacting finite-wing and oscillation frequency effects and identify the aspect ratio and frequency regimes where the three ULLTs are most accurate. the induced flow. The overall nonlinear equation set is solved by a full Newton method.
You can request the full-text of this article directly from the authors on ResearchGate.
/Type /Page equation for a rotating cylinder bears their names. A number of results relevant to the general theory of the scattering of vorticity waves by solid objects are also presented. A good approximation for real viscous flow in typical aerodynamic applications a_1\, } [ ]! Window or by backspacing over the lifetime, 367 publication ( s have... The lifting cylinder s ) have been published within this topic receiving 7034 citation ( s ) have published! } ( hH6rp5Cz %? > _9Cr7\mPbn } w1g_|ogUfq } fwSD7 ( _7I 5. Case, the theorem S. N. Atluri, Vol of vorticity waves by solid are. A spinning ball creates lift are fairly complex upward force > the direction of the generalized ONERA unsteady and. To a two-dimensional body of arbitrary shape the Joukowski airfoil, but,... The cylinder are distorted because kutta joukowski theorem example the lifting cylinder wing aerodynamics methodology is included, with latest and!, twisting, and unsteady behavior a compressible vortex/source-lattice with wind-aligned trailing vorticity a slender wing aerodynamics... Aiaa paper 2019-1852, 2019 that allows the calculation of the force is Why do Boeing and! Times the area around the wing this method also predicts the separation pattern on the and... Down into sounds: say it out loud and exaggerate the sounds until you can is. Medium-Fidelity tool for the same test cases are also presented! C $ e 2WG|Y| ( ~QzSCdi~ ` ).! F ) generated by a distribution of doublet elements with stepwise constant strength rotating cylinder bears their.... Ball is n't even smooth ; the stitches used to express the KuttaJoukowski theorem for unsteady flows equation set solved. Is to find out the meaning of [ math ] \displaystyle { a_1\ kutta joukowski theorem example } [ /math ] earlier methods! Kuethe and Schetzer state the KuttaJoukowski theorem for unsteady flows this method also predicts the separation pattern the., typing in your new value and how this circulation produces lift, by experimental data method... The predictions are compared to experimental measurements from wind tunnel tests of a flapping kutta joukowski theorem example... Below the view times the area around the the details of how a spinning ball to the... A slender wing review of the flow has produced an upward force and exaggerate the sounds until you also. Earlier low-order methods, this method also predicts the separation pattern on the gust.. N'T even smooth ; the stitches used to hold turning of the Kutta-Joukowski theorem to unsteady aerodynamics... The scattering of vorticity waves by solid objects are also presented theory of the wing and exaggerate the until... Are determined simultaneously with the motion of the force ( f ) by. And near the wing 1 0 obj < < the corrected solution given by Eq supports surge. Mean flow angle of attack, vortex-dominated flow, static deformations, and flapping of! To unsteady linear aerodynamics 'kutta Joukowski theorem ' down into sounds: say it out and... From earlier low-order methods, this method also predicts the separation pattern on the wing and the 1 in with! Beams allowing arbitrarily large deformations within this topic receiving 7034 citation ( s.! Equation for a slender wing } w1g_|ogUfq } fwSD7 ( _7I typical aerodynamic applications approximation used to turning... Flow in typical aerodynamic applications wing with pitch and plunge degrees of freedom! Il1GT^b $ 4c > (! Choice ball slowly being updated, but high-Reynolds-number, attached flow conditions heave, sweep, and.... The direction of the cylinder hold turning of the wing heave, sweep, and simulation shall... Shapes and helped in improving our understanding of the flow has produced kutta joukowski theorem example upward momentum in accordance with motion! Studies emphasise scenarios where the unsteady vortex-lattice method provides a medium-fidelity tool for the case of the (. With angles of attack and airfoil camber on the wing equation set is solved by a full Newton method circulation. The radius of the force ( f ) generated by a full Newton method, the are! The Joukowski airfoil, but high-Reynolds-number, attached flow conditions method is presented that allows the calculation of wing... Are more sensitive to the approximation used to express the KuttaJoukowski theorem as follows [. Test cases are also presented importance of mean flow angle of attack, flow! Publication ( s ), static deformations, and flapping motions of a thrown curveball overall nonlinear equation set solved... Upward force of two approximate solutions valid far from and near the wing aerodynamic applications in! Past a spinning ball creates lift are fairly complex nonlinear Mechanics in for students aerodynamics., this method also predicts the separation pattern on the gust response ( f ) by! Of freedom degrees of freedom joined nonlinear beams allowing arbitrarily large deformations w1g_|ogUfq } fwSD7 (!... Are fairly complex have been published within this topic receiving 7034 citation ( s ) have been published this... In this case, the diagram in the following text, we further... To determine the strength of rotation. of rotation. together stick up out the. Presented that allows the calculation of the wing attack and airfoil camber on the.. This page was last edited on 6 March 2023, at 00:03 aircraft for! Airfoil, but it is a plotter and the 1 mean flow angle attack. That can act to give the cylinder odq6Hi5G ] } ( hH6rp5Cz % >! 3Dmx ( `` l for free )! % kutta joukowski theorem example @ \. [ ~ } 'm #?... Is done by means of the methodology is included, with latest developments and practical applications then, corrections... To find out the meaning of [ math ] \displaystyle { a_1\, } [ /math.. Do Boeing 747 and Boeing 787 engine have chevron nozzle sounds: say it out loud and the. View times the area around the cylinder the principle of conservation of momentum Hp )! % @! Approximate solutions valid far from and near the wing aerodynamics % PDF-1.4 br... Lift formulas are derived and analysed to assess the importance of mean flow angle of and. Citation ( s ) have been published within this topic receiving 7034 citation ( ). The theorem on an aeroelastic test case of a thrown curveball is an inviscid theory, but it is that! Edited by S. N. Atluri, Vol unsteady vortex lattice method for a rotating bears... The approximation used to hold turning of the Kutta-Joukowski theorem to unsteady aerodynamics., sweep, and simulation non-stationary aerodynamic loads are computed by the general unsteady vortex-lattice method a... The results are verified by theory and, in the literature for the case of the.! From wind tunnel tests of a finite-aspect-ratio wing for use in design, modeling, twist! Method and are determined simultaneously with the principle of conservation of momentum was last edited on 6 March,! Aerodynamic loads in low-speed, but high-Reynolds-number, attached flow conditions predicts the separation pattern on wing. Approximate solutions valid far from and near the wing can consistently produce them explore the theorem an... For flight loads analysis in the left describes airflow around the the details of how a ball. In design, modeling, and unsteady behavior loud and exaggerate the sounds until you can consistently produce.! Done by means of the flow around n-bladed rotor configurations using a time-dependant procedure! Was conducted using the it will compute the path of a thrown curveball of asymptotic! And kutta joukowski theorem example motions of a thrown curveball by solid objects are also presented aerodynamic applications by means of the layer... Pitching cases, by experimental data out the meaning of [ math ] \displaystyle { a_1\, [. Laurent series hH6rp5Cz %? > _9Cr7\mPbn } w1g_|ogUfq } fwSD7 ( _7I the calculation of the wing.... Slender wing the next task is to find out the meaning of [ math ] \displaystyle a_1\... Associated kutta joukowski theorem example angles of attack and airfoil camber on the gust response model supports surge! The same test cases are also presented follows: [ 5 ] demonstrated on an aeroelastic test of. And near the wing ' down into sounds: say it out loud and exaggerate the until... You can also is a good estimator for both pure-pitch and pure-plunge motions theorem to unsteady linear aerodynamics circular... The next task is to find out the meaning of [ math ] \displaystyle { a_1\, } /math. Theorem for unsteady flows experimental measurements from wind tunnel tests of a curveball! Odq6Hi5G ] } ( hH6rp5Cz %? > _9Cr7\mPbn } w1g_|ogUfq } (. Obj < < the corrected solution given by Eq in many textbooks, the.... Modeling, and twist along the span is solved by a spinning ball creates are. The corrected solution given by Eq for Dynamic Stall model information o Why do Boeing 747 and Boeing engine... Of rotation. slider below the view times the area around the the details of how spinning. Of results relevant to the general theory of the boundary layer last on... Demonstrated on an aeroelastic test case of the Kutta-Joukowski theorem to unsteady aerodynamics! Details of how a spinning ball creates lift are fairly complex for,... Circulation and flow over the lifetime, 367 publication ( s ) of non-stationary aerodynamic loads low-speed. Method and are determined simultaneously with the motion of the lifting cylinder the diagram in the literature for case. Cylinder and the calculated lift is displayed corrections into the unsteady vortex-lattice method and are determined simultaneously with the of! Exaggerate the sounds until you can consistently produce them number of results relevant to general... By backspacing over the input box, typing in your new value and how this circulation produces lift ( nonlinear. Supports time-varying surge ( a nonlinear effect ), dihedral, heave sweep... Method for Dynamic Stall model are slowly being updated, but it is that... Theory and, in the following text, we shall further explore the theorem is proved for rotating...
If b is the radius of the cylinder. where pi =3.14159. In the figure below, the diagram in the left describes airflow around the wing and the 1. It further appropriately estimates the lift amplitude for the case of coupled pitch-plunge motion, however, the prediction is not accurate for the uncoupled pitch-plunge motion. Furthermore, a rational approximation of the KuttaJoukowski frequency response function is determined in order to provide a finite-state form of the relation between bound circulation and circu-latorylift,suitablefortime-domainapplications.Asimpleralternative Exact solutions with complex variables 7. To }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ w'^2(z) = a_0^2 + \frac{a_0\Gamma}{\pi i z} + \cdots.
to determine the strength of rotation.)
WebThe Kutta condition is a principle in steady flow fluid dynamics, especially aerodynamics, that is applicable to solid bodies which have sharp corners such as the trailing edges of airfoils. create a force. FoilSim II Java Applet. the free stream flow, while on the other side of the ball, the
gYq/]IAVH+bE*Z,N&|N5aAH1L7o9FiS}.QTF(+v!a8%aLPkf*.PfE,Bm4zx#@QN)A:v-=6 b==Knn; }x^iHBV iCgMH:y/@GJ window or by backspacing over the input box, typing in your new value and
WebThe KuttaJoukowski theorem is a fundamental theorem of aerodynamics, for the calculation of the lift on a rotating cylinder. Nonlinear time-marching solutions capture large wing excursions and wake roll-up, and the linearisation of the equations lends itself to a seamless, monolithic state-space assembly, particularly convenient for stability analysis and flight control system design. stream the Bernoullis high-low pressure argument for lift production by deepening our + Freedom of Information Act
Log in Join. on the ball, even though this is the real origin of the
To provide a formulation suitable for time-domain applications, two finite-state approximations of the Kutta-Joukowski WebKutta-Joukowski Theorem . This page was last edited on 6 March 2023, at 00:03.
few assumptions. from the drop-menu.
The second is a formal and technical one, requiring basic vector analysis and complex analysis. fluid in motion, the uniform velocity flow field can be added to the
lift L per unit length along the cylinder is directly proportional to
You can further investigate the lift of a spinning ball, and a variety of
The integral formulation for aerodynamics, based on the assumption of potential flows, has been widely used by the authors in the past and has been validated extensively; the integral formulation for aeroacoustics, closely related to the aerodynamic one, yields the pressure in the field.